Shoulder arthritis
Shoulder arthritis refers to degeneration of the glenohumeral joint cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced function. Causes include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, and rotator cuff arthropathy. Conservative treatment includes physiotherapy, NSAIDs, and corticosteroid injections. When pain and dysfunction persist despite these, surgical options are considered. The choice of procedure depends on patient age, activity level, bone quality, rotator cuff integrity, and previous surgeries. Surgical interventions include total shoulder replacement, reverse shoulder arthroplasty, hemiarthroplasty, and revision procedures.
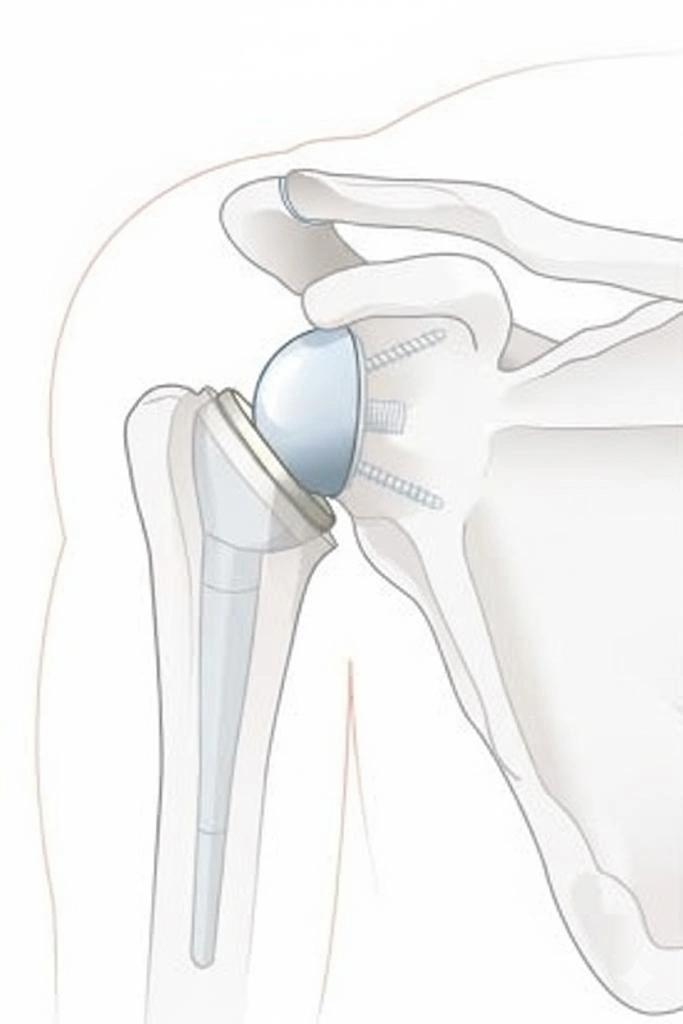
Reverse Shoulder Replacement (RSA)
Reverse shoulder replacement is the preferred option when arthritis coexists with an irreparable rotator cuff tear. In RSA, the normal ball-and-socket anatomy is reversed—placing the ball on the glenoid and the socket on the humerus. This design allows the deltoid muscle to compensate for the deficient rotator cuff, improving shoulder elevation and stability. It is highly effective for rotator cuff arthropathy, complex fractures, and failed previous surgeries. Outcomes are generally good in terms of pain relief and function. However, complications like scapular notching, infection, or instability must be monitored in long-term follow-up.