Shoulder dislocation (instability)
Hill-Sachs Lesion
Remplissage
Remplissage is an arthroscopic procedure designed to address engaging Hill-Sachs lesions, which are compression fractures of the posterolateral humeral head caused during anterior shoulder dislocation. This technique fills the defect using the infraspinatus tendon and posterior capsule, converting the intra-articular defect into an extra-articular one. As a result, the humeral head no longer engages with the glenoid rim during movement. It is often performed in conjunction with Bankart repair in patients with off-track lesions. Remplissage helps restore stability without the need for more invasive bony procedures and is effective in low- to moderate-level bone defects.
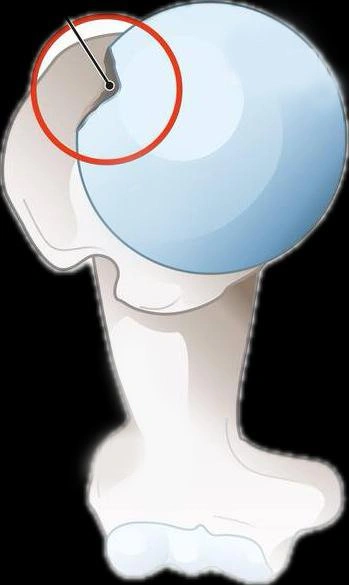
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting for Hill-Sachs lesions is reserved for deep or large defects that compromise stability or when remplissage is insufficient. This approach involves placing autograft or allograft bone into the humeral head defect to restore its sphericity. The goal is to prevent engagement with the glenoid rim, especially in bipolar lesions. It may be required in revision surgeries or high-demand patients with recurrent instability. Techniques include open or arthroscopic graft placement, with care to avoid overstuffing the joint. Accurate sizing and fixation of the graft are essential for long-term success and return to full shoulder function.